“Change is your friend, not your foe; change is a brilliant opportunity to grow.” — Simon T. Bailey
“If you always do what you’ve always done, you’ll always be where you’ve always been.” — T.D. Jakes
These quotes define the beauty of the Scaled Agile Framework. The cornerstone aspect of the Scaled Agile Framework and one of the pillars of the House of Lean is about continuously improving and not being afraid to acclimate to change. Improvement leads to growth as it gives you an opportunity to learn new dimensions and new ways one thing can be done. SAFe promotes confidence to adapt and keep up with the evolving and changing needs.
At the end of every Program Increment, there is an Inspect and Adapt session.
It is a perfect opportunity to reflect on the mistakes made and how to make sure they are not made again. Indeed an integral part of SAFe, the backlog items are improved and are added which enhance velocity, quality and the reliability of the next Program Increment. The participants of this session include all the Program Stakeholders, Product Management, Business Owners, Agile Teams, Release Train Engineers and System and Solution Architect.
An Inspect and Adapt session consists of the following events:
- System Demo
- Quantitative Measurement
- Retrospective
- Problem Solving Workshop
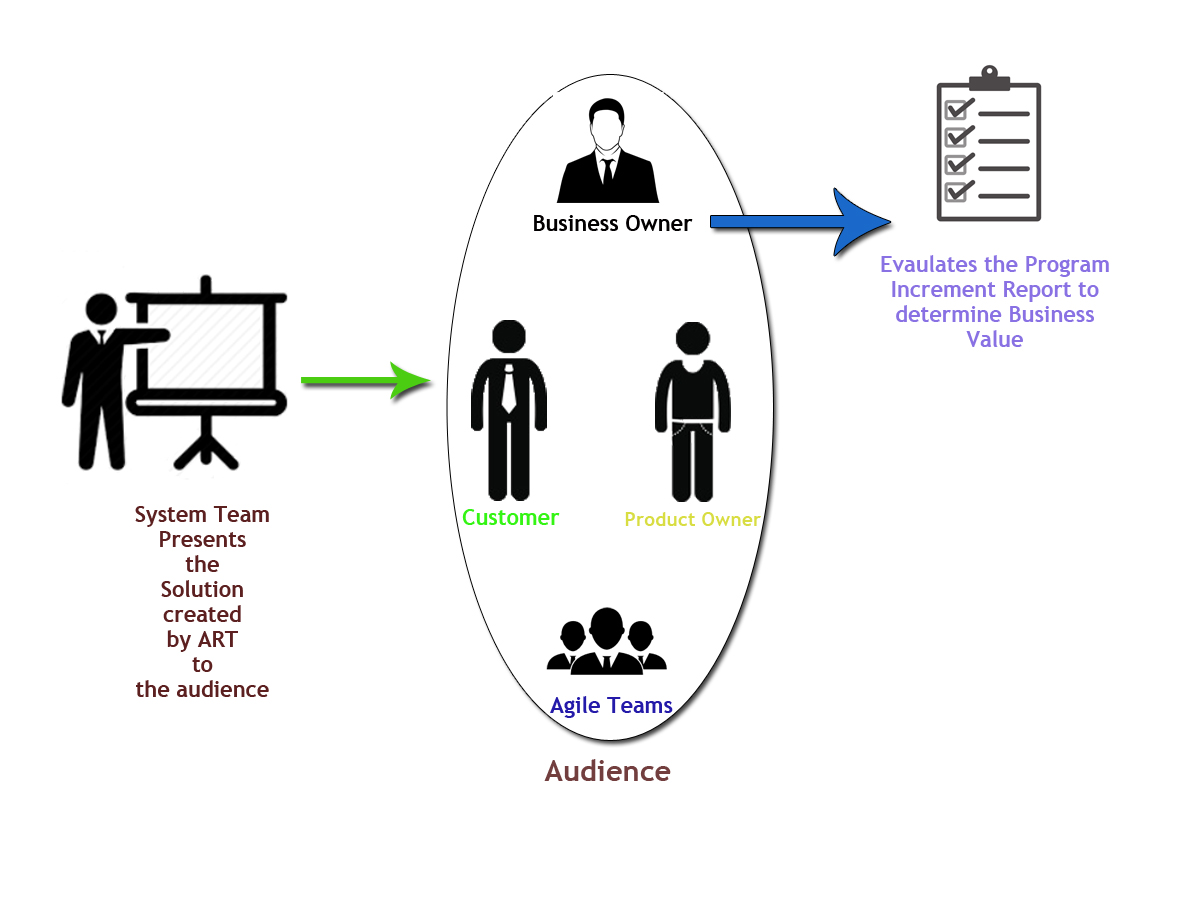
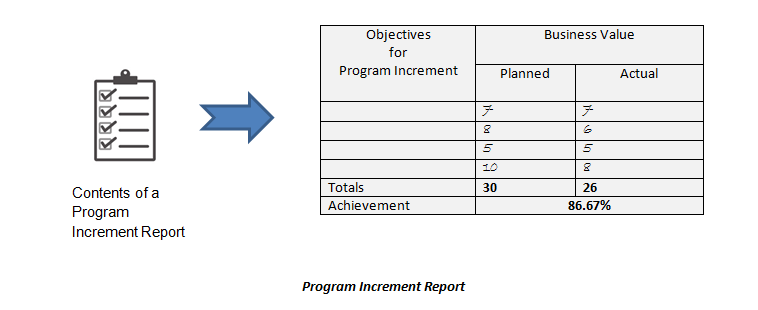
Inspect and Adapt is started by the System Demo. It is an event with proper staging and caters to a larger audience. It demonstrates the solution that has been developed by the Agile Release Train. Presented by the one of the representatives of the System Team, the audience consists of all the stakeholders, business owners, customers, and agile teams. The time for the session is set to last for an hour. It is led by Product Management or system team and is facilitated by the Release Train Engineer. By evaluating the Program Increment Performance Report, the business owners rate the business value to get the achievement percentage. This report has the list of objectives of the Program Increment and against those features are two set of values. One is the Planned Value and the second is the Actual Value. The sum of the values in each set is added. The total of each set is then used to calculate the achievement percentage.
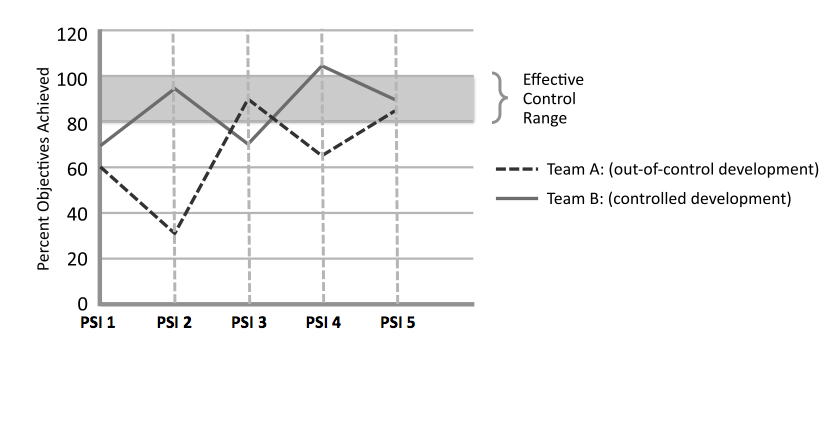
Following the previous event is the Quantitative Measurement. The most common measure is the Program Predictability Measure. This information is gathered by the Release Train Engineer. Using the results from the Program Increment Performance Report, graphs are plotted which shows the percentage of objectives achieved in every Program Increment. These trends are compared with the values that were originally planned. The performance rate should be between 80-100% which suggests optimum flow. These findings are analyzed and help in identifying any issues. The picture below represents the Quantitative Measurement.
Now that the significant problems are identified by the teams, it is time to address which ones to solve first. The retrospective session lasts for 30 minutes where the teams can solve a problem from a program level or team level. This session is attended by important stakeholders of the Agile Release Train including business owners, customers and the management. The problems are selected by the team, usually from the program level. Once the problem has been decided, it is solved in a cross functional and a collaborative manner as the team works to solve the problem assisted by other team members working on the same problem. Smaller problems are generally rectified in this session. And if the magnitude of the problem is big, then a Problem Level Workshop is held.
A Problem Level Workshop is organized by the Release Train Engineer which incorporates the Root Cause Analysis method to solve large problems at the Program Level. The duration of this workshop is of 2 hours.
The following steps describe the procedure of how this is done:
- Begins with first clearly stating and then agree to solve the problem.
- Then apply Root Cause Analysis in which a fish-bone diagram is constructed that states the problem at the head of it and the branches of it are the processes, people, tools or programs that lead to the problem.
- Now identify the biggest root cause using Pareto analysis which is a technique in which team members vote on the root cause producing the significant effect.
- Now the new problem is restated clearly and then finding a solution for them by brainstorming.
- Once a solution is reached, the items in the backlog are improved and to be used in the next Program Increment.